2024 Mid-Year Report: Pricing Trends in the Industrials Sector
The industrials sector has experienced significant shifts in pricing dynamics in the first half of 2024. Three key trends shaping the landscape are persistent cost volatility, localized responses to macroeconomic trends, and increasing commercial complexity.
These trends are driven by a variety of factors and have profound implications for how industrials companies should think about pricing.
In this report, we'll dive into each of the trends in more detail, explore their implications for pricing, and close with key actions industrials companies should take to best compete and win in the back half of 2024.
Trend #1: Persistent Cost Volatility
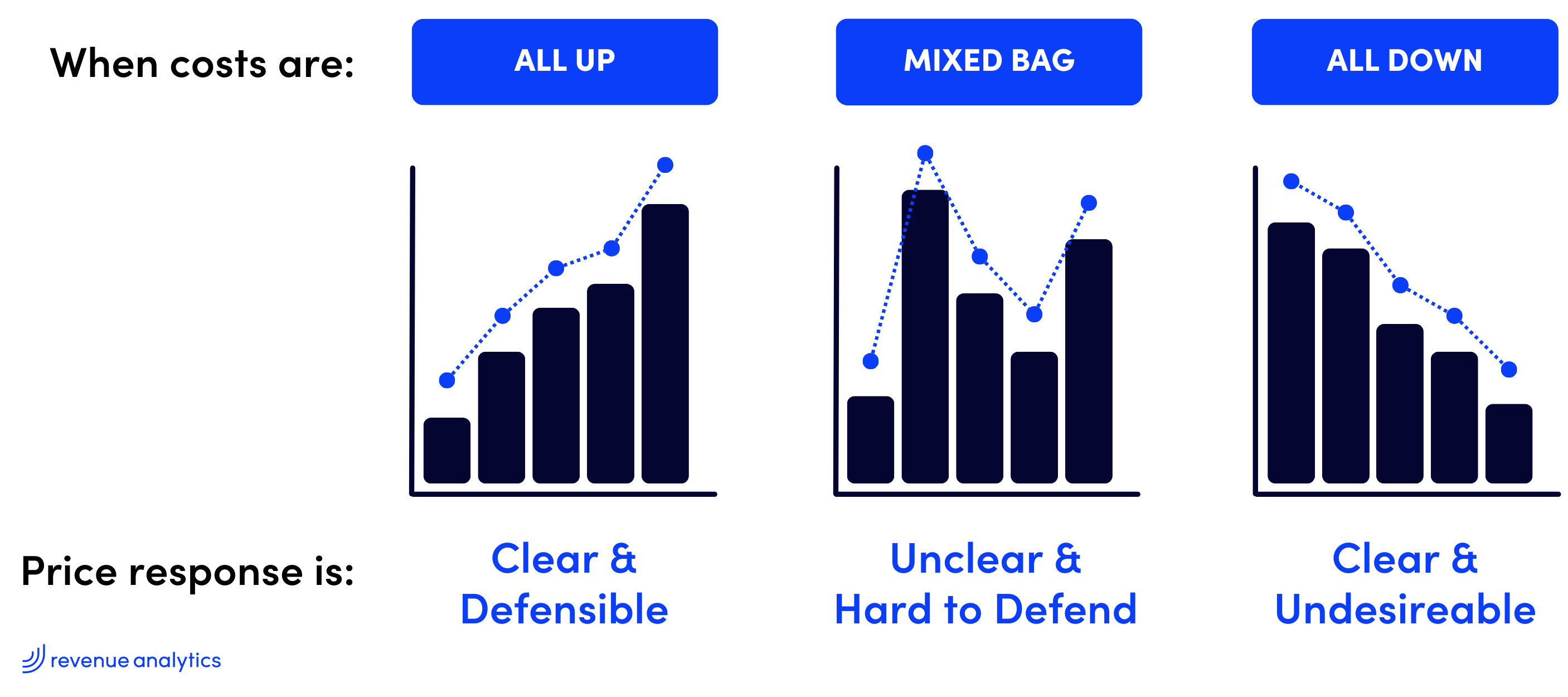
Cost volatility in the industrials sector remains a critical challenge, driven by fluctuations in raw material prices, labor rates, and transportation costs, to name a few.
-
Raw Material Price Fluctuations: So far in 2024, commodity price movements have been a mixed bag. Lumber prices ran up in the first quarter but have come back down (Trading Economics). In metals, aluminum prices are up 14% YTD, steel prices have dropped nearly 10% YTD, and copper is up 17% YTD (Trading Economics). Finally, in resins, spot polypropylene prices have risen $0.11/lb. YTD and polymer-grade propylene is up $0.16/lb. YTD (Plastics Today).
-
Total Labor Rates: Labor rates in the industrials sector have seen a significant rise, with wages and salaries up 4.4% so far this year (Bureau of Labor Statistics). This is driven by a combination of skilled labor shortages and inflationary pressures. The manufacturing sector reported a 5% increase in average wages, while the construction sector saw a 7% rise due to high demand for skilled workers (World Bank). Additionally, health insurance and other worker-related costs have all increased, further contributing to the overall rise in total labor costs.
-
Transportation Costs: Costs are generally flat to slightly up across domestic transportation modes and remain elevated year-over-year. Geopolitical unrest (and the impact on oil prices), driver shortages, and logistical challenges should be closely watched in the back half of 2024 (DAT Freight & Analytics).
Why is all this volatility a challenge for pricing? More frequent, targeted, and efficient price updates will be required to keep margins stable and growing. Throughout the course of 2024, most industrials companies are likely to experience a variety of different input cost scenarios to navigate.
Trend #2: Localized Response to Macroeconomic Trends
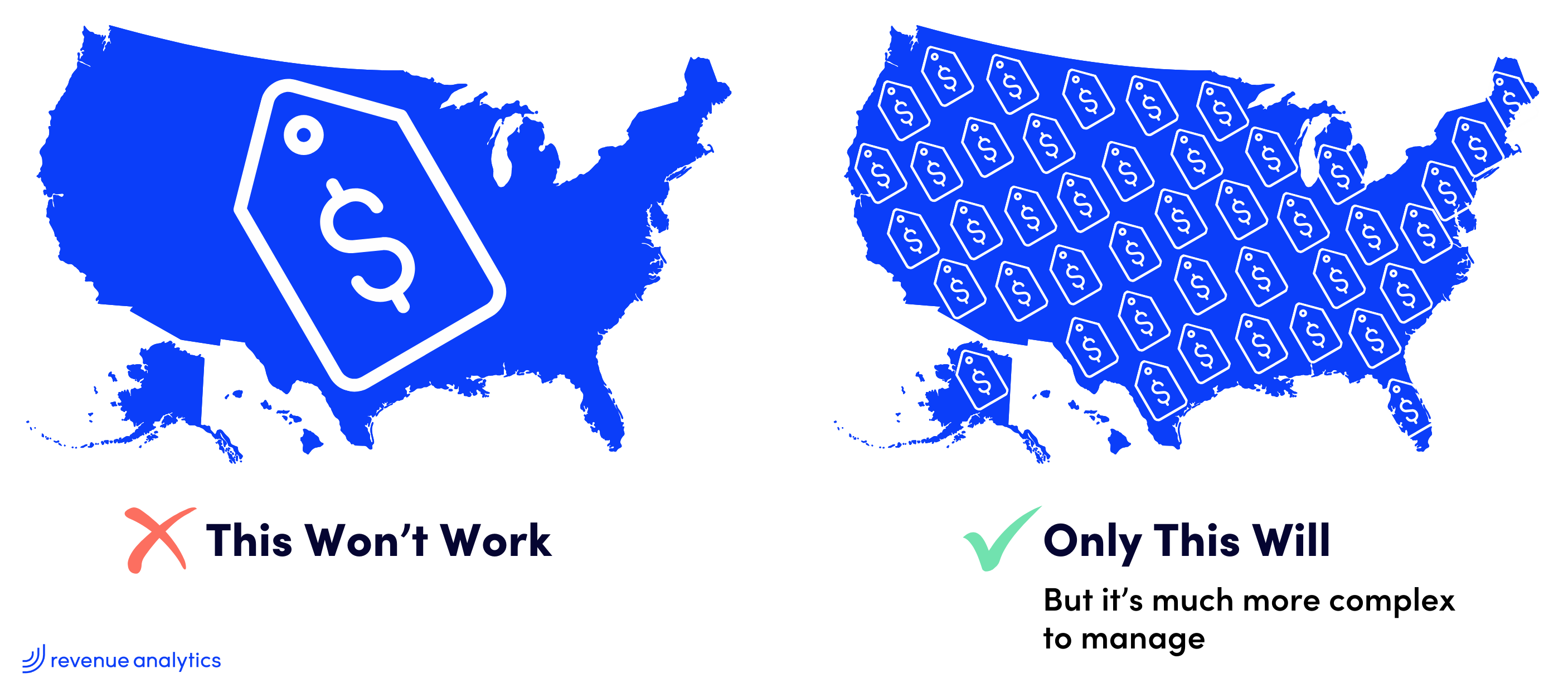
Industrials companies are increasingly adapting their pricing strategies to local market conditions, driven by macroeconomic factors such as infrastructure spending, housing starts, and e-commerce growth, as evidenced by 2024 data. These trends, however, are experienced unevenly across different micro-markets, each responding uniquely to broader economic shifts.
-
Infrastructure Spending on Construction Equipment: The US government's infrastructure spending has led to an 8% increase in demand for construction equipment. This surge has caused prices for heavy machinery to rise by 7%, as manufacturers adjust to heightened demand and increased production costs. However, the impact varies across regions — urban areas with major infrastructure projects see higher demand and price increases, while rural areas experience more moderate effects (Ryerson) (World Bank).
-
Housing Starts on Building Materials: April US housing starts popped 5.7% compared to March but are down slightly from the same time last year (US Census Bureau). After a runup in lumber prices to begin the year, prices have come down 17% in the last two months. Volatility in housing starts is exacerbated when looking across local markets, where clear regional patterns give way to the fact that in any given town the demand can be drastically different just a few miles down the road. This localized variation has a ripple effect through demand, and subsequently pricing, for lumber and other related building products (Trading Economics).
-
E-commerce on Packaging: The continued growth of e-commerce, which has increased by 12% in 2024, has led to higher demand for packaging materials. Prices for cardboard and packaging supplies increased by 9%, driven by supply chain disruptions and rising raw material costs. Urban centers with higher concentrations of e-commerce businesses see steeper price increases, whereas regions with less online retail activity experience more stable pricing (World Bank).
Why are vast differences in localized response a challenge for pricing? Because it requires a far more granular approach to price setting to account for all the localized nuances, which compounds the complexity.
Trend #3: Increasing Commercial Complexity
The industrials sector is facing growing complexity in commercial transactions, influenced by selling more products, expanding sales channels, and meeting higher customer expectations, as illustrated by 2024 trends.
-
Selling More Products Than Ever Before: Many industrial companies have been busy extending their product lines to capture a greater share of the wallet or penetrate new markets. This expansion can drive growth, but more products across more categories and locations increases the complexity of price management.
-
Selling Through More Channels: Companies are also adding more sales channels to their go-to-market strategy via direct sales, through distribution, and/or on e-commerce platforms. While adding a new sales channel can unlock growth, it also requires a different pricing structure. Independently, each channel's pricing may be manageable. But as more customers shop across channels, the interrelationship becomes far more complex to manage.
-
Selling to Customers with Higher Expectations: Customers' expectations seem to only go in one direction, up. And that's no different in 2024, especially coming off an extended period of increasing prices. Combine that with the continued trends of business-to-business customers expecting business-to-consumer-type personalization and the pricing equation multiplies quickly.
Each initiative adds a layer of complexity that's manageable, but still a lot. The real pricing challenge comes from the compounding effect when you stack multiple of these initiatives over time.

Strategies for Industrials Companies
To navigate these pricing trends, industrials companies can adopt several strategic pricing actions:
-
Set More Granular Prices: By leveraging data analytics, companies can develop more granular pricing strategies that reflect the specific costs and demand conditions of individual products and services across varied markets and customer bases. This approach allows for more precise pricing adjustments and better alignment with market conditions.
-
Update Prices More Frequently: Given the rapid pace of change in costs and market conditions, companies should consider updating their prices more frequently. Pricing technology can help in making timely adjustments, ensuring that prices remain competitive and reflective of current market realities.
-
Measure Results for Continuous Improvement: It's crucial to measure the impact of pricing changes and continuously refine pricing strategies. By tracking key performance indicators such as sales volume, profit margins, and sales team compliance to the pricing strategy, companies can identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to optimize pricing.
In conclusion, the industrials sector in 2024 is navigating a complex pricing environment characterized by cost volatility, localized economic responses, and commercial complexity. By adopting more granular pricing, updating prices frequently, and measuring results for continuous improvement, companies can better manage these challenges and capitalize on opportunities in a dynamic market.
To learn more about how to address these emerging trends, book a 1:1 with an industrials pricing expert.

